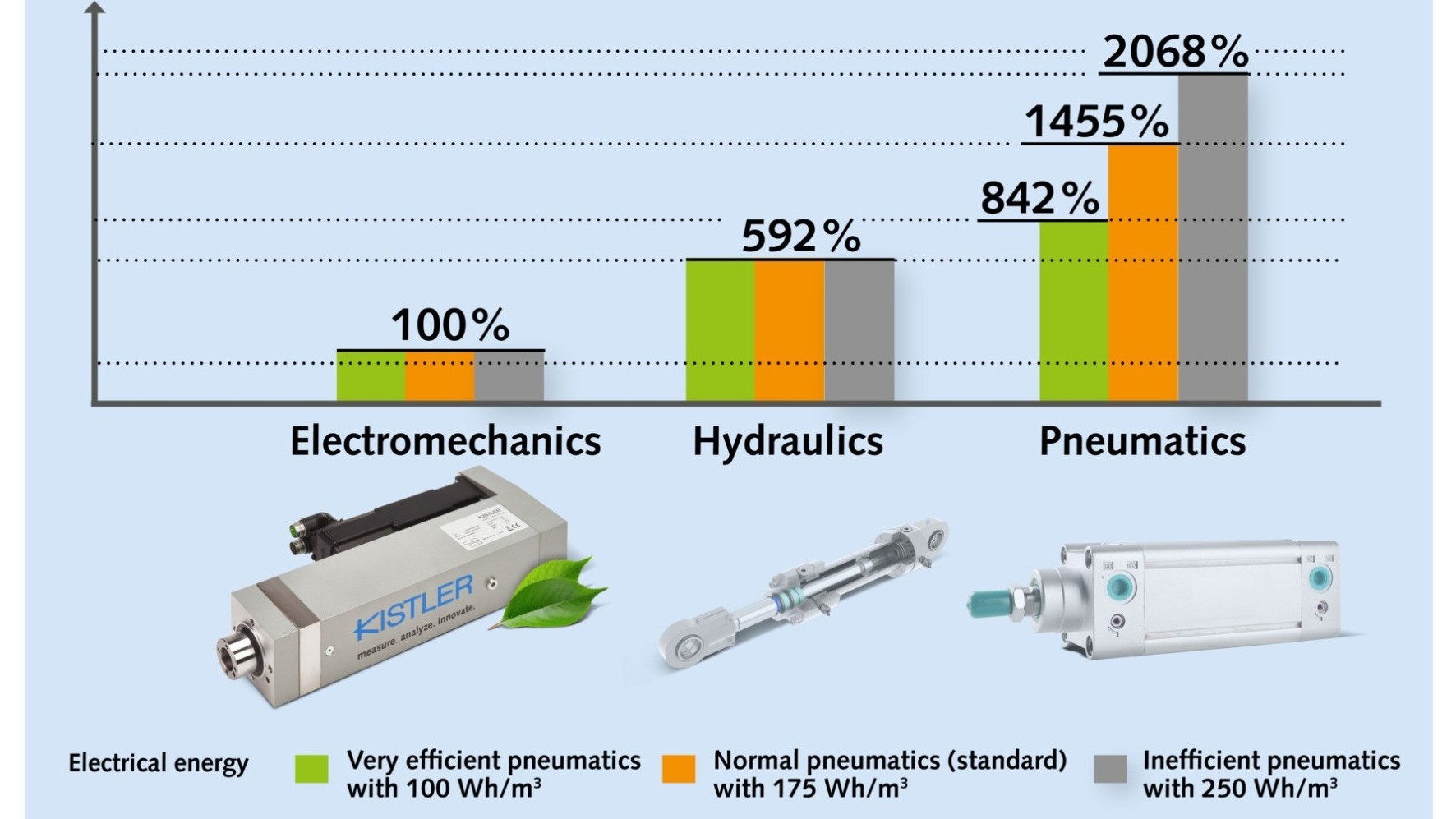
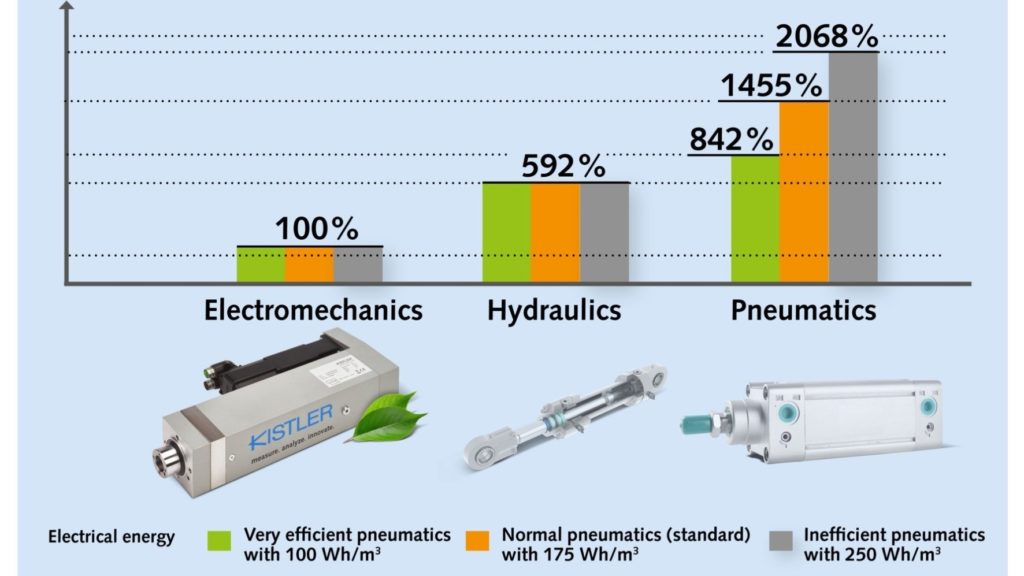
Winterthur, November 2024 – As part of a commissioned study by Kistler, researchers at Ostfalia University of Applied Sciences investigated the energy efficiency of three joining processes with different drive technologies – electromechanical joining systems as well as hydraulic and pneumatic ones. The results show that the electromechanical variant is the most efficient in terms of joining work alone, i.e. the joining stroke. Joining processes with electromechanical systems are up to 5.9 times more energy-efficient than their hydraulic variant. The pneumatic joining system has the highest energy consumption: depending on the efficiency of the compressed air system, it consumes between 8.4 and 20.6 times more energy than the electromechanical alternative.